5.3 Cyber Security
Security Threats
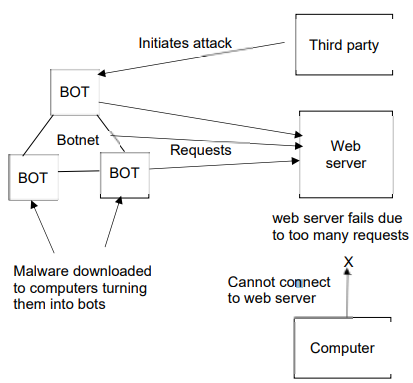
Denial Of Service
- Malware downloaded to several computers
- turning It into a bot/zombie
- creating a network of bots/zombies
- Third party/hacker initiating the attack
- Bots send requests to a web server at the same time
- The web server falls due to the requests
- Legitimate requests cannot reach the web server
Aims of a DDOS Attack
- Revenge
- To affect a company's reputation
- Entertainment value
- To demand a ransom to stop it
- To test a system's resilience
Solution?
- Proxy server
- Firewall
- Users scanning their computers with anti-malware
Annotation of Denial Of Service Attack
Phishing
- legitimate looking email sent to user
- encourages user to click a link that directs user to a fake website
- User encouraged to enter personal details into a fake website // designed
- to obtain personal details from a user
Solution?
- always check browser url
- Make use of antivirus/anti-malware software. Perform regular scans
Pharming
- Malicious code/malware is downloaded/installed // software downloaded
- without users' knowledge
- that re-directs user to fake website (when legitimate URL entered)
- User encouraged to enter personal details into a fake website // designed
- to obtain personal details from a user
Solution?
- avoid opening emails from unknown senders
- check emails for inconsistent logos, grammatical mistakes
- check sender email address for incorrect spelling
Brute Force Attack
- used to crack an account password
- systematically try all the different combinations of letters, numbers and other symbols with the purpose of finding an account password
- Makes use of word lists
- Intention of gaining unauthorised access to accounts/systems
Solution?
- use of two factor authentication
- Use of strong + unpredictable passwords
Data Interception
- a form of stealing data by tapping into a wired or wireless communication link
- can be carried out using a packet sniffer
- The intercepted data is sent back to the hacker
- wireless data interception can be carried out using wardriving
Solution?
- Encryption on Files (will not prevent but can make attackers effort to steal data harder)
- Use of Firewall
- Use of WEP (encryption protocol for wireless networks)
Hacking
- Gaining unauthorised access to a computer system without the owners permission
- Can lead to identity theft
- Can lead to data being deleted
- Can lead to data being corrupted
Solution?
- Use of a firewall
- Encryption of files (will not prevent but can make attackers effort to steal data harder)
- Make use of strong passwords
Social Engineering
- when a cybercriminal creates a social situation that can lead to a potential victim dropping their guard
- It involves the manipulation of people into breaking their normal security procedures and not following best practice
Different social engineering threats
- Instant messaging-Malicious links are embedded into instant messages
- Scareware-This is often done using a pop-up message that claims that the user’s computer is infected with a virus; the user is told they need to download the fake anti-virus immediately
- Emails/phishing scams-The user is tricked by the apparent genuineness of an email and opens a link in the email; this redirects their browser to a fake website
- Baiting-The cybercriminal leaves a malware-infected memory stick somewhere where it can be found; the finder picks up the memory stick and plugs it into their computer (just to see who it belongs to) and unwittingly downloads malicious malware
- Phone calls-For example, a so-called IT professional calls the user on their mobile claiming their device has been compromised in some way; the user is advised to download some special software that allows the cybercriminal to take over the user’s device giving them access to personal information
Solution?
- User education on such threats to keep users cautious in these situations
Malware
Virus
- Programs or program code that replicate (copies themselves) with the intention of deleting or corrupting files, or causing a computer to malfunction
- Must be triggered by the activation of a host.
- Often sent as email attachments
Solution for Virus
- Never open emails from unknown sources
- Don’t install non-original software
- Always run up-to date virus scanner
Worm
- Stand alone malware that can self-replicate. Intention is to spread to other computers and corrupt whole networks
- They remain inside applications which allows them to move throughout networks.
- Worms replicate without targeting and infecting specific files on a computer
- rely on security failures within networks to permit them to spread unhindered.
Adware
- flood an end-user with unwanted advertising
- Not harmful
- Highlight weaknesses in user’s security defences
- Hard to remove – as it is difficult to determine whether or not it is harmful
- Hijack a browser and create its own default search requests
Trojan horse
- Is a program which is often disguised as legitimate software but with malicious instructions embedded within it.
- Replaces all or part of the legitimate software with the intent of carrying out some harm to the user’s computer system.
- Usually arrives as an email attachment or are downloaded from an infected website and must be executed by the end user.
- Once installed into the user’s computer, it will give cyber criminals access to personal information
Spyware
- Sotware that gathers information by monitoring key presses
- Information collected is sent back to the attacker
- Software may allow other spyware to be installed to read cookie data and change user default web browser
Solution for Spyware
- Use of anti-spyware software
- using a mouse to select characters from passwords rather than typing
- using an on screen keyboard for entering passwords
Ransomware
- Programs that encrypt data on a user’s computer and hold the data hostage.
- It will lock your screen until the demands of the cyber criminals have been met.
- The cyber criminal waits until the ransom money is paid and sometimes the decryption key is then sent to the user.
- It can be installed on a user’s computer by way of a Trojan horse or through social engineering
Solution for Ransomware
- make use of anti-virus/anti-malware software
- Always run up-to date virus scanner
Solutions for security threats
Access Levels
- Providing users with different permission for the data
- Limiting access to reading data// limiting the data that can be viewed
- Limiting access to editing data
- Normally linked to a username
Antivirus/Antispyware
- Scans files for viruses // detects/identifies a virus
- Can constantly run in background
- Can run a scheduled scan
- Can automatically updating virus definitions
- Can quarantine a virus
- Can delete a virus
- Completes heuristic checking
- Notifies user of a possible virus
Authentication (passwords)
- Use of strong passwords when creating accounts
- Passwords should not be short in length (eg 8 characters)
- passwords should use upper and lowercase
- passwords should contain symbols(eg. !$#&)
- password attempts should be limited(eg. not allow the user to re-enter a password for a set time period after 3 failed attempts, this prevents brute force attacks)
Authentication (two-step verification)
- Requires two methods of authentication to verify a user
- user enters a password..
- ..and a secret combination of characters sent to an email assigned to the account
- access is granted when both are correct
- often used with online payments and signing into accounts
Firewall/Proxy
- Checks all incoming and outgoing traffic
- store whitelist/blacklist ip addresses
- Can block incoming/outgoing signals
- Can block unauthorised access
- keeps logs of all traffic
- Can be hardware OR software (OR Both)
Difference between Firewall and Proxy
- Proxy can hide a users IP address, a firewall does not hide the users ip address
- Proxy intention is to divert an attack from a server, a firewall is to stop anauthorised access
- proxy examins requests for a website but a firewall does not
- proxy allows faster access to a web page using cache but a firewall does not
- proxy can hide internal network from internet but a firewall cannot
Biometrics
- Fingerprint: 1) very easy to use. 2) small storage requirements.3) can make mistakes if skin is dirty or damaged.4) considered intrusive as it is used in criminal identification
- Retina: 1)High accuracy as the human retina cannot be replicated.2)Relatively slow to verify a retina.3)Very expensive to install and setup
- Facial Recognition: 1)non-intrusive method.2)relatively inexpensive.3)can be affected by many factors such as lighting aging,glasses etc
- Voice Recognition: 1)Non-intrusive. 2)Quick verification time 3)relatively inexpensive. 4)low accuracy, a cold can change a persons voice.5)peoples voices can be recorded to trick voice recognition.
SSL
- Secure sockets Layer
- It encrypts data being transmitted
- Makes use of public and private keys