3.2 INPUT and OUTPUT devices
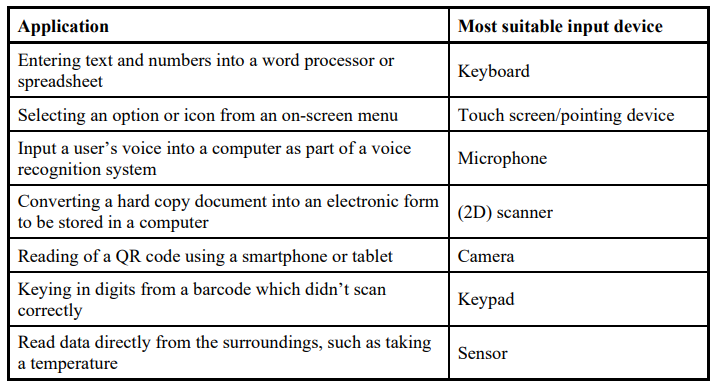
What is an input device?
- Hardware device used to provide data and control signals to a computer
What is an output device?
- Hardware devices that allow information to be sent out of a computer system
Common input devices
- Barcode Scanner
- Digital Camera
- Microphone
- Optical Mouse
- QR Scanner
Advantages of using QR Codes in a Supermarket
- No need to price each item individually
- automatic stock control
- Faster checkouts as items are immediately scanned
- Fewer errors in bills
Common output devices
- Actuators
- Inkjet,laser, 3D printer
- LED,LCD screen
- Speaker
Uses of digital cameras
- reading QR codes on a smartphone
- video conferencing
- robots, where information about surroundings is needed
DLP Advantages
- higher contrast ratios
- greater longevity
- quieter running
DLP Disadvantages
- The image tends to suffer from ‘shadowing’ during moving images
- They do not have grey components in the image
- Colour definition is not as good as LCD projectors
Inkjet Printer Pros & Cons
- produce high-quality photo/vivid colour images
- don’t need to warm up
- very low purchase price compared to laser printers
- have a small ink reservoir
- not suitable for long print runs (ink cartridges can be used up quickly)
- small paper trays
- Slower prints per minute compared to laser
Laser Printer Pros & Cons
- have large paper trays for long print runs
- have large capacity toner cartridges
- very quiet printing
- cost per page is very low
- expensive to maintain (toner is expensive)
- not suitable for printing high quality pictures
- High up front cost (compared to inkjet)
Uses of a 3D Printer
- Prosthetic Limbs
- making prototypes
- fashion and art
Which printer?
- Laser printer: high volume printouts
- Inkjet printer: High Quality image printouts
- 3D printer: printing models/prosthetics
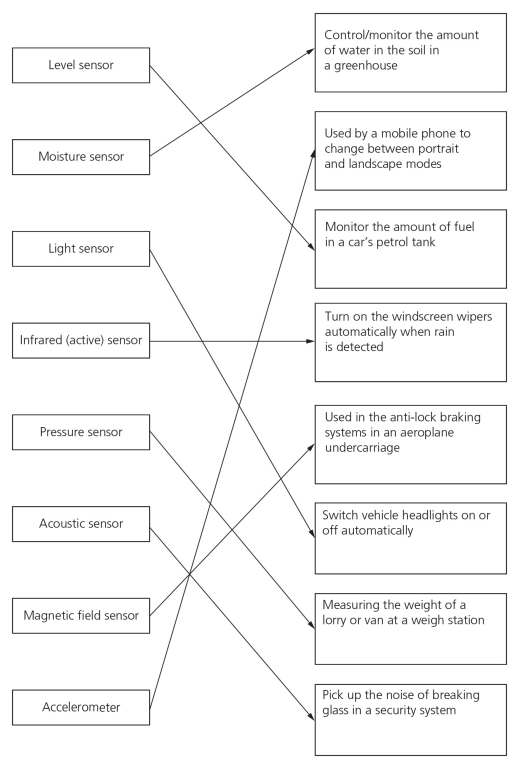
Sensors
- Acoustic- measures the level of sound in an environment
- Accelerometer-measures the acceleration forces
- Flow-measures the amount of liquid or gas flowing through or around an environment
- Gas- measures the presence and concentration of a gas in the atmosphere
- Humidity-measures the level of moisture in the atmosphere
- Infra-red-measures infra-red radiation
- Level-measures whether a substance such as a liquid is at a certain level or amount
- Light-measures the ambient light in a certain environment
- Magnetic field-measures the presence of magnetic field that may be emitted by an object
- Moisture-measures the amount of water that is presence in a substance
- pH- measures the pH level of a substance
- Pressure- measures the force of pressure that is applied to the sensor or device
- Proximity- measures how close an object is in comparison to the sensor
- Temperature-measures the temperature of an object or substance